Observação: no momento, não há suporte para os executores hospedados no GitHub no GitHub Enterprise Server. Você pode ver mais informações sobre o suporte futuro planejado no GitHub public roadmap.
Visão geral de exemplo
Este artigo usa um fluxo de trabalho de exemplo para demonstrar alguns dos principais recursos de CI do GitHub Actions. Quando esse fluxo de trabalho é disparado, ele executa automaticamente um script que verifica se o site Docs do GitHub tem links desfeitos.
O diagrama a seguir mostra uma visão de alto nível das etapas do fluxo de trabalho e como elas são executadas no trabalho:
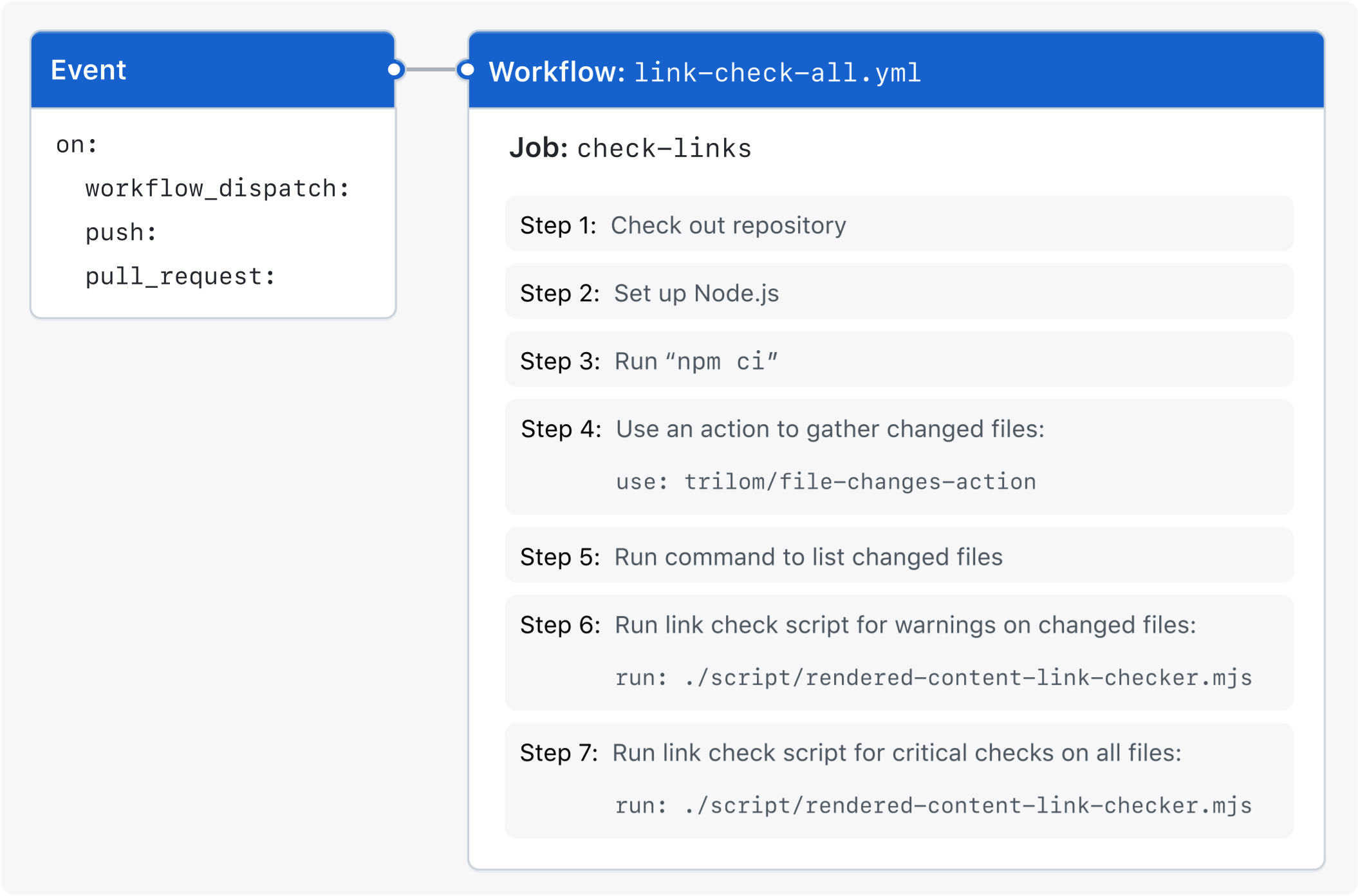
Recursos usados neste exemplo
O fluxo de trabalho de exemplo demonstra os seguintes recursos do GitHub Actions.
| Recurso | Implementação |
|---|---|
| Como disparar um fluxo de trabalho a ser executado automaticamente | push |
| Como disparar um fluxo de trabalho a ser executado automaticamente | pull_request |
| Como executar um fluxo de trabalho manualmente usando a interface do usuário | workflow_dispatch |
| Definir permissões para o token | permissions |
| Como controlar quantas execuções de fluxo de trabalho ou trabalhos podem ser executadas ao mesmo tempo | concurrency |
| Como executar o trabalho em diferentes executores, dependendo do repositório | runs-on |
Como instalar o node no executor | actions/setup-node |
| Como usar uma ação de terceiros | trilom/file-changes-action |
Fluxo de trabalho de exemplo
O fluxo de trabalho a seguir foi criado pela equipe de engenharia de Docs do GitHub. Para revisar a versão mais recente deste arquivo no repositório github/docs, confira check-broken-links-github-github.yml.
O fluxo de trabalho a seguir renderiza o conteúdo de todas as páginas da documentação e verifica todos os links internos para garantir que eles se conectem corretamente.
# Isso define o nome do fluxo de trabalho, conforme ele será exibido na guia "Ações" do repositório do GitHub repository.
name: 'Link Checker: All English'
# The `on` key lets you define the events that trigger when the workflow is run. You can define multiple events here. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-workflows/triggering-a-workflow#using-events-to-trigger-workflows)."
on:
# Add the `workflow_dispatch` event if you want to be able to manually run this workflow from the UI. For more information, see [`workflow_dispatch`](/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#workflow_dispatch).
workflow_dispatch:
# Add the `push` event, so that the workflow runs automatically every time a commit is pushed to a branch called `main`. For more information, see [`push`](/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#push).
push:
branches:
- main
# Add the `pull_request` event, so that the workflow runs automatically every time a pull request is created or updated. For more information, see [`pull_request`](/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#pull_request).
pull_request:
# This modifies the default permissions granted to `GITHUB_TOKEN`. This will vary depending on the needs of your workflow. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-jobs/assigning-permissions-to-jobs)."
#
# In this example, the `pull-requests: read` permission is needed for the `trilom/file-changes-action` action that is used later in this workflow.
permissions:
contents: read
pull-requests: read
# The `concurrency` key ensures that only a single workflow in the same concurrency group will run at the same time. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-jobs/using-concurrency)."
# `concurrency.group` generates a concurrency group name from the workflow name and pull request information. The `||` operator is used to define fallback values.
# `concurrency.cancel-in-progress` cancels any currently running job or workflow in the same concurrency group.
concurrency:
group: '${{ github.workflow }} @ ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.label || github.head_ref || github.ref }}'
cancel-in-progress: true
# The `jobs` key groups together all the jobs that run in the workflow file.
jobs:
# This line defines a job with the ID `check-links` that is stored within the `jobs` key.
check-links:
# The `runs-on` key in this example configures the job to run on a GitHub-hosted runner or a self-hosted runner, depending on the repository running the workflow.
#
# In this example, the job will run on a self-hosted runner if the repository is named `docs-internal` and is within the `github` organization. If the repository doesn't match this path, then it will run on an `ubuntu-latest` runner hosted by GitHub. For more information on these options, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-jobs/choosing-the-runner-for-a-job)."
runs-on: ${{ fromJSON('["ubuntu-latest", "self-hosted"]')[github.repository == 'github/docs-internal'] }}
# The `steps` key groups together all the steps that will run as part of the `check-links` job. Each job in a workflow has its own `steps` section.
steps:
# The `uses` key tells the job to retrieve the action named `actions/checkout`. This is an action that checks out your repository and downloads it to the runner, allowing you to run actions against your code (such as testing tools). You must use the checkout action any time your workflow will use the repository's code or you are using an action defined in the repository.
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
# This step uses the `actions/setup-node` action to install the specified version of the Node.js software package on the runner, which gives you access to the `npm` command.
- name: Setup node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 16.13.x
cache: npm
# The `run` key tells the job to execute a command on the runner. In this example, `npm ci` is used to install the npm software packages for the project.
- name: Install
run: npm ci
# This step uses the `trilom/file-changes-action` action to gather all the changed files. This example is pinned to a specific version of the action, using the `a6ca26c14274c33b15e6499323aac178af06ad4b` SHA.
#
# In this example, this step creates the file "${{ env.HOME }}/files.json", among others.
- name: Gather files changed
uses: trilom/file-changes-action@a6ca26c14274c33b15e6499323aac178af06ad4b
with:
fileOutput: 'json'
# To help with verification, this step lists the contents of `files.json`. This will be visible in the workflow run's log, and can be useful for debugging.
- name: Show files changed
run: cat $HOME/files.json
# This step uses the `run` command to execute a script that is stored in the repository at `script/rendered-content-link-checker.mjs` and passes all the parameters it needs to run.
- name: Link check (warnings, changed files)
run: |
./script/rendered-content-link-checker.mjs \
--language en \
--max 100 \
--check-anchors \
--check-images \
--verbose \
--list $HOME/files.json
# This step also uses `run` command to execute a script that is stored in the repository at `script/rendered-content-link-checker.mjs` and passes a different set of parameters.
- name: Link check (critical, all files)
run: |
./script/rendered-content-link-checker.mjs \
--language en \
--exit \
--verbose \
--check-images \
--level critical
name: 'Link Checker: All English'Isso define o nome do fluxo de trabalho, conforme ele será exibido na guia "Ações" do repositório do GitHub repository.
on:The on key lets you define the events that trigger when the workflow is run. You can define multiple events here. For more information, see "Acionando um fluxo de trabalho."
workflow_dispatch:Add the workflow_dispatch event if you want to be able to manually run this workflow from the UI. For more information, see workflow_dispatch.
push:
branches:
- mainAdd the push event, so that the workflow runs automatically every time a commit is pushed to a branch called main. For more information, see push.
pull_request:Add the pull_request event, so that the workflow runs automatically every time a pull request is created or updated. For more information, see pull_request.
permissions:
contents: read
pull-requests: readThis modifies the default permissions granted to GITHUB_TOKEN. This will vary depending on the needs of your workflow. For more information, see "Atribuindo permissões aos trabalhos."
In this example, the pull-requests: read permission is needed for the trilom/file-changes-action action that is used later in this workflow.
concurrency:
group: '${{ github.workflow }} @ ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.label || github.head_ref || github.ref }}'
cancel-in-progress: trueThe concurrency key ensures that only a single workflow in the same concurrency group will run at the same time. For more information, see "Usando simultaneidade."
concurrency.group generates a concurrency group name from the workflow name and pull request information. The || operator is used to define fallback values.
concurrency.cancel-in-progress cancels any currently running job or workflow in the same concurrency group.
jobs:The jobs key groups together all the jobs that run in the workflow file.
check-links:This line defines a job with the ID check-links that is stored within the jobs key.
runs-on: ${{ fromJSON('["ubuntu-latest", "self-hosted"]')[github.repository == 'github/docs-internal'] }}The runs-on key in this example configures the job to run on a GitHub-hosted runner or a self-hosted runner, depending on the repository running the workflow.
In this example, the job will run on a self-hosted runner if the repository is named docs-internal and is within the github organization. If the repository doesn't match this path, then it will run on an ubuntu-latest runner hosted by GitHub. For more information on these options, see "Escolhendo o executor para um trabalho."
steps:The steps key groups together all the steps that will run as part of the check-links job. Each job in a workflow has its own steps section.
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4The uses key tells the job to retrieve the action named actions/checkout. This is an action that checks out your repository and downloads it to the runner, allowing you to run actions against your code (such as testing tools). You must use the checkout action any time your workflow will use the repository's code or you are using an action defined in the repository.
- name: Setup node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 16.13.x
cache: npmThis step uses the actions/setup-node action to install the specified version of the Node.js software package on the runner, which gives you access to the npm command.
- name: Install
run: npm ciThe run key tells the job to execute a command on the runner. In this example, npm ci is used to install the npm software packages for the project.
- name: Gather files changed
uses: trilom/file-changes-action@a6ca26c14274c33b15e6499323aac178af06ad4b
with:
fileOutput: 'json'This step uses the trilom/file-changes-action action to gather all the changed files. This example is pinned to a specific version of the action, using the a6ca26c14274c33b15e6499323aac178af06ad4b SHA.
In this example, this step creates the file "${{ env.HOME }}/files.json", among others.
- name: Show files changed
run: cat $HOME/files.jsonTo help with verification, this step lists the contents of files.json. This will be visible in the workflow run's log, and can be useful for debugging.
- name: Link check (warnings, changed files)
run: |
./script/rendered-content-link-checker.mjs \
--language en \
--max 100 \
--check-anchors \
--check-images \
--verbose \
--list $HOME/files.jsonThis step uses the run command to execute a script that is stored in the repository at script/rendered-content-link-checker.mjs and passes all the parameters it needs to run.
- name: Link check (critical, all files)
run: |
./script/rendered-content-link-checker.mjs \
--language en \
--exit \
--verbose \
--check-images \
--level criticalThis step also uses run command to execute a script that is stored in the repository at script/rendered-content-link-checker.mjs and passes a different set of parameters.
# Isso define o nome do fluxo de trabalho, conforme ele será exibido na guia "Ações" do repositório do GitHub repository.
name: 'Link Checker: All English'
# The `on` key lets you define the events that trigger when the workflow is run. You can define multiple events here. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-workflows/triggering-a-workflow#using-events-to-trigger-workflows)."
on:
# Add the `workflow_dispatch` event if you want to be able to manually run this workflow from the UI. For more information, see [`workflow_dispatch`](/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#workflow_dispatch).
workflow_dispatch:
# Add the `push` event, so that the workflow runs automatically every time a commit is pushed to a branch called `main`. For more information, see [`push`](/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#push).
push:
branches:
- main
# Add the `pull_request` event, so that the workflow runs automatically every time a pull request is created or updated. For more information, see [`pull_request`](/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#pull_request).
pull_request:
# This modifies the default permissions granted to `GITHUB_TOKEN`. This will vary depending on the needs of your workflow. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-jobs/assigning-permissions-to-jobs)."
#
# In this example, the `pull-requests: read` permission is needed for the `trilom/file-changes-action` action that is used later in this workflow.
permissions:
contents: read
pull-requests: read
# The `concurrency` key ensures that only a single workflow in the same concurrency group will run at the same time. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-jobs/using-concurrency)."
# `concurrency.group` generates a concurrency group name from the workflow name and pull request information. The `||` operator is used to define fallback values.
# `concurrency.cancel-in-progress` cancels any currently running job or workflow in the same concurrency group.
concurrency:
group: '${{ github.workflow }} @ ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.label || github.head_ref || github.ref }}'
cancel-in-progress: true
# The `jobs` key groups together all the jobs that run in the workflow file.
jobs:
# This line defines a job with the ID `check-links` that is stored within the `jobs` key.
check-links:
# The `runs-on` key in this example configures the job to run on a GitHub-hosted runner or a self-hosted runner, depending on the repository running the workflow.
#
# In this example, the job will run on a self-hosted runner if the repository is named `docs-internal` and is within the `github` organization. If the repository doesn't match this path, then it will run on an `ubuntu-latest` runner hosted by GitHub. For more information on these options, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-jobs/choosing-the-runner-for-a-job)."
runs-on: ${{ fromJSON('["ubuntu-latest", "self-hosted"]')[github.repository == 'github/docs-internal'] }}
# The `steps` key groups together all the steps that will run as part of the `check-links` job. Each job in a workflow has its own `steps` section.
steps:
# The `uses` key tells the job to retrieve the action named `actions/checkout`. This is an action that checks out your repository and downloads it to the runner, allowing you to run actions against your code (such as testing tools). You must use the checkout action any time your workflow will use the repository's code or you are using an action defined in the repository.
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
# This step uses the `actions/setup-node` action to install the specified version of the Node.js software package on the runner, which gives you access to the `npm` command.
- name: Setup node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 16.13.x
cache: npm
# The `run` key tells the job to execute a command on the runner. In this example, `npm ci` is used to install the npm software packages for the project.
- name: Install
run: npm ci
# This step uses the `trilom/file-changes-action` action to gather all the changed files. This example is pinned to a specific version of the action, using the `a6ca26c14274c33b15e6499323aac178af06ad4b` SHA.
#
# In this example, this step creates the file "${{ env.HOME }}/files.json", among others.
- name: Gather files changed
uses: trilom/file-changes-action@a6ca26c14274c33b15e6499323aac178af06ad4b
with:
fileOutput: 'json'
# To help with verification, this step lists the contents of `files.json`. This will be visible in the workflow run's log, and can be useful for debugging.
- name: Show files changed
run: cat $HOME/files.json
# This step uses the `run` command to execute a script that is stored in the repository at `script/rendered-content-link-checker.mjs` and passes all the parameters it needs to run.
- name: Link check (warnings, changed files)
run: |
./script/rendered-content-link-checker.mjs \
--language en \
--max 100 \
--check-anchors \
--check-images \
--verbose \
--list $HOME/files.json
# This step also uses `run` command to execute a script that is stored in the repository at `script/rendered-content-link-checker.mjs` and passes a different set of parameters.
- name: Link check (critical, all files)
run: |
./script/rendered-content-link-checker.mjs \
--language en \
--exit \
--verbose \
--check-images \
--level critical
Próximas etapas
- Para aprender sobre o GitHub Actions, confira "Entendendo o GitHub Actions".
- Para obter um guia passo a passo de criação de um fluxo de trabalho básico, confira "Início rápido para GitHub Actions".
- Se você já entende os conceitos básicos do GitHub Actions, saiba mais sobre os fluxos de trabalho e seus recursos em "Sobre fluxos de trabalho".